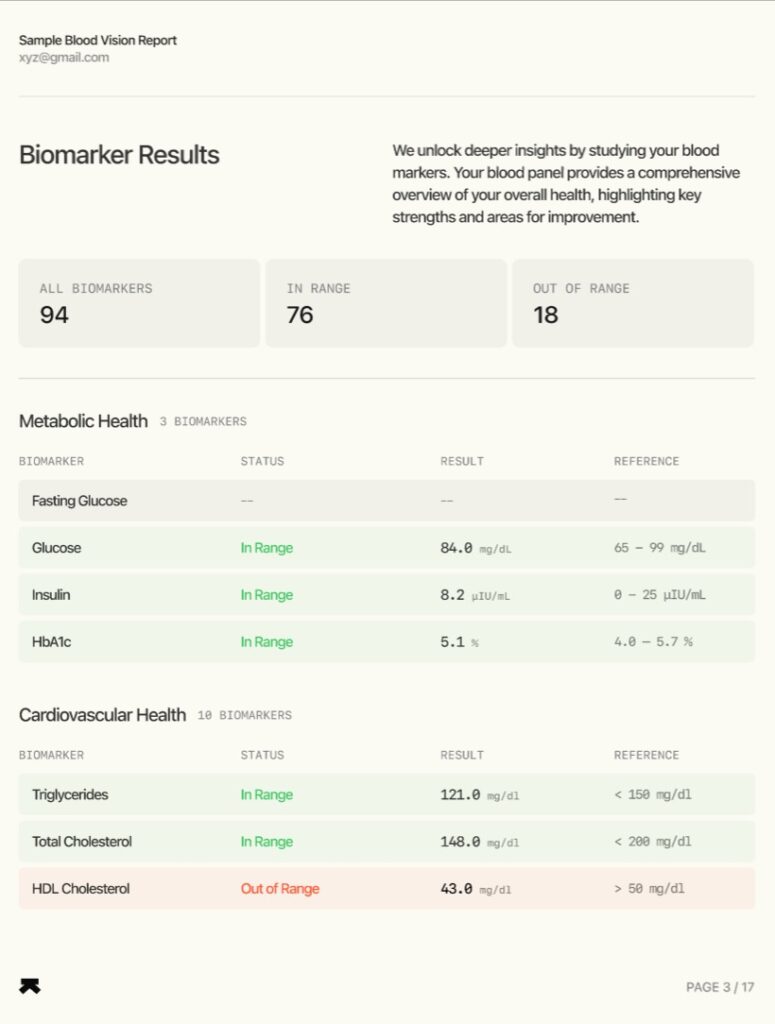
The Metabolic Health panel in Blood Vision helps assess your risk of developing conditions like diabetes – a disease that, when left unmanaged, can lead to serious complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, and vision loss.
The good news is that early detection, using preventative health blood tests such as Blood Vision, allows for early action. Many people can reverse or delay metabolic dysfunction through targeted lifestyle changes.
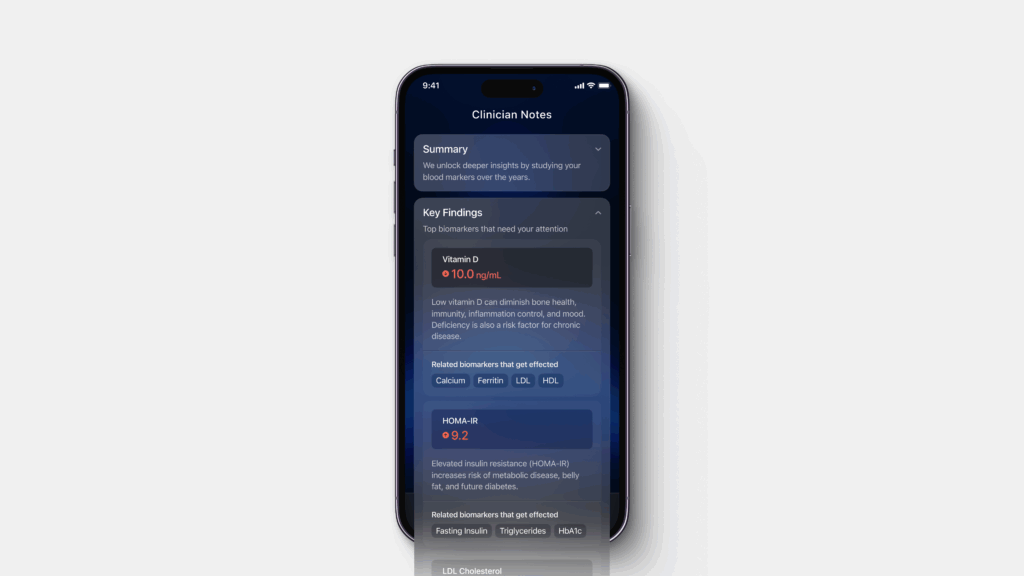
This panel tracks critical markers, such as fasting glucose, HbA1c, and insulin levels, giving you a window into how well your body regulates blood sugar. Understanding these markers empowers you to take proactive steps before diabetes sets in.
Let’s break down the key tests in this panel and why they matter:
Revealed: 10 cardiovascular blood markers and what they mean
Blood Vision Metabolic Health Panel: Glucose Regulation Markers
| Marker | What It Measures | Why It Matters | Healthy Range (Blood Vision Standard) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fasting Glucose | Blood sugar levels after an 8+ hour fast | Detects early signs of impaired glucose regulation — a potential indicator of prediabetes or diabetes | 70–100 mg/dL (Men & Women) |
| Fasting Insulin | Insulin levels in the blood after fasting | Elevated levels may suggest insulin resistance, a silent precursor to type 2 diabetes and metabolic dysfunction | 2.3–26.0 µIU/mL (Men & Women) |
| HbA1c | Average blood glucose over the past 2–3 months | Elevated HbA1c reflects chronic blood sugar issues and increases the risk of nerve, kidney, and cardiovascular complications | Under 5.7% (Women; Green Zone = <5.7%) |
| HOMA-IR | Estimated insulin resistance (calculated from fasting glucose and insulin values) | A high score indicates reduced insulin sensitivity, often seen in early metabolic syndrome and before diabetes fully develops | Under 2.0 (Women) |
Glucose regulation metrics
Fasting Glucose
The fasting glucose test measures your blood sugar levels after you’ve gone at least 8 hours without food. Elevated results can indicate impaired glucose regulation — a warning sign of diabetes or prediabetes.
Why it matters: Blood sugar affects everything from energy levels to mood and long-term health. This test is a frontline tool in catching blood sugar issues early.
Healthy range: 70–100 mg/dL (Blood Vision standard for both men and women)
Fasting Insulin
This test measures the amount of insulin in your bloodstream after fasting. If levels are high, it may suggest your body is becoming resistant to insulin’s effects — a key warning sign for developing type 2 diabetes.
Why it matters: Insulin resistance often develops silently. Detecting it early can help prevent full-blown metabolic dysfunction.
Healthy range: 2.3–26.0 µIU/mL (Blood Vision standard for both men and women)
HbA1c (Hemoglobin A1c)
HbA1c reflects your average blood sugar over the past 2–3 months, making it a more long-term indicator than a single fasting glucose reading.
Why it matters: Elevated HbA1c suggests your body is struggling with chronic blood sugar control, increasing your risk for nerve, kidney, and cardiovascular damage.
Healthy range: Under 5.7% (Blood Vision standard for women; green zone = <5.7%)
HOMA-IR (Homeostatic Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance)
HOMA-IR is a calculated score that estimates your level of insulin resistance based on fasting glucose and insulin values.
Why it matters: A high HOMA-IR score signals your body is having difficulty using insulin efficiently — a precursor to metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes.
Healthy range: Under 2.0 (Blood Vision standard for women)
Summary
You don’t need a diabetes diagnosis to benefit from understanding these markers. Many people live with early-stage insulin resistance or elevated glucose without realizing it. By getting tested, you can take targeted action — through diet, exercise, or medical support — before the damage sets in.
If you’re concerned about your long-term metabolic health, a comprehensive blood panel for diabetes risk is one of the best tools available to take control early.